TEMPOS VERBAIS EM INGLÊS

Tempos Verbais em Inglês
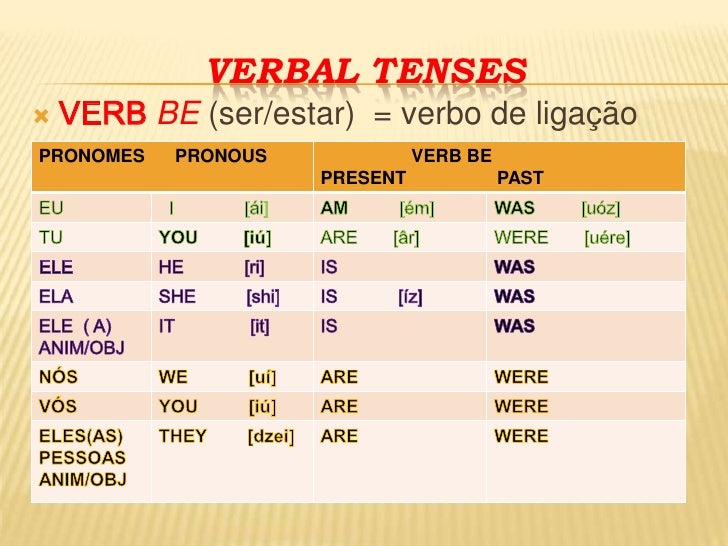
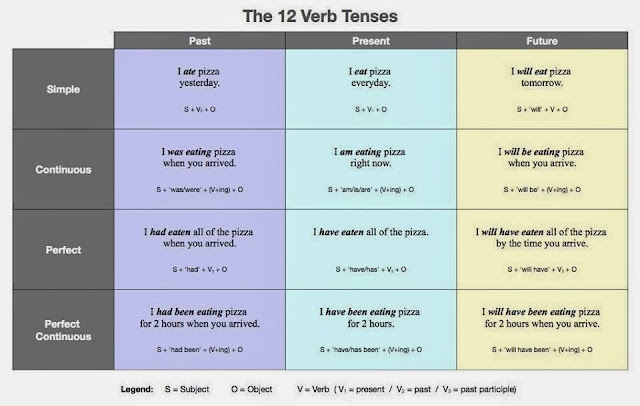
No inglês, os verbos e tempos verbais (Verbs and Tenses) são classificados em:
Simple Present (Presente Simples): descreve uma ação habitual e atual ocorrida no presente. No português, esse tempo verbal é chamado de Presente do Indicativo.
Veja abaixo a tabela com o verbo to love (amar) conjugado no Simple Present:
| I | love |
| you | love |
| he/she/it | loves |
| we | love |
| you | love |
| they | love |
Exemplos:
- She loves him. (Ela o ama.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Does she love him? (Ela o ama?) - INTERROGATIVE
- She doesn’t love him. (Ela não o ama.) - NEGATIVE
Present Continuous or Present Progressive (Presente Contínuo ou Progressivo): descreve uma ação que está ocorrendo no presente, no momento em que se fala.
Esse tempo verbal é formado com o verbo auxilar to be no Simple Present (presente simples) + o gerúndio (-ing) do verbo principal.
Veja abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Present Continuous:
| I | am loving |
| you | are loving |
| he/she/it | is loving |
| we | are loving |
| you | are loving |
| they | are loving |
Exemplos:
- They are loving the book. (Eles estão amando o livro.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Are they loving the book? (Eles estão amando o livro?) - INTERROGATIVE
- They aren’t loving the book. (Eles não estão amando o livro.) - NEGATIVE
Simple Past (Passado Simples): expressa ações passadas, ou seja, descreve os fatos que já aconteceram.
A formação desse tempo verbal ocorre pela repetição das formas regulares acrescidas de –d ou –ed, enquanto os irregulares não seguem a forma padrão.
Para entender melhor, veja aqui a lista de verbos regulares e irregulares no inglês. Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo regular to love (amar) no Simple Past:
| I | loved |
| you | loved |
| he/she/it | loved |
| we | loved |
| you | loved |
| they | loved |
Exemplos:
- He loved her. (Ele a amou.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Did he love her? (Ele a amou?) - INTERROGATIVE
- He didn’t love her. (Ele não a amou.) - NEGATIVE
Past Continuous or Past Progressive (Passado Contínuo ou Progressivo): expressa uma ação que estava ocorrendo no passado.
Ele é formado pela união do verbo auxilar to be no Simple Past (passado simples) + o gerúndio (-ing) do verbo principal.
Veja abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Past Continuous:
| I | was loving |
| you | were loving |
| he/she/it | was loving |
| we | were loving |
| you | were loving |
| they | were loving |
Exemplos:
- He was loving the trip. (Ele estava amando a viagem.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Was he loving the trip? (Ele estava amando a viagem?) - INTERROGATIVE
- He wasn’t loving the trip. (Ele não estava amando a viagem.) - NEGATIVE
Simple Future (Futuro Simples): expressa ações que irão ocorrer, ou seja, que ainda não aconteceram.
É formado pelo auxiliar modal will + o infinitivo do verbo principal sem “to”. Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Simple Future:
| I | will love |
| you | will love |
| he/she/it | will love |
| we | will love |
| you | will love |
| they | will love |
Exemplos:
- They will love to travel. (Eles amarão viajar.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Will they love to travel? (Eles amarão viajar?) - INTERROGATIVE
- They won’t love to travel. (Eles não amarão viajar.) - NEGATIVE
Future Continuous or Progressive (Futuro Progressivo ou Contínuo): expressa ações que estarão ocorrendo no futuro, ou seja, descreve um fato que acontecerá em um momento específico no futuro.
Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Future Continuous, formado pelo Simple Future do verbo to be (will be) + gerúndio (-ing) do verbo principal:
| I | will be loving |
| you | will be loving |
| he/she/it | will be loving |
| we | will be loving |
| you | will be loving |
| they | will be loving |
Exemplos:
- She will be loving the trip by this time next year. (Ela estará amando a viagem por esta altura no ano que vem.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Will she be loving the trip by this time next year? (Ela estará amando a viagem por esta altura no ano que vem?) - INTERROGATIVE
- She won’t be loving the trip by this time next year. (Ela não estará amando a viagem por esta altura no ano que vem.) - NEGATIVE
Formas Verbais do Tempo Perfeito (Verb Forms of the Perfect Tense)
As formas verbais do tempo perfeito em inglês são formadas com o verbo auxiliar to have (have/has) conjugado + o Past Participle (particípio passado) do verbo principal. Elas são classificadas em:
Present Perfect Simple (Presente Perfeito Simples): expressam ações influenciadas pelo presente e que ainda estão acontecendo ou que terminaram recentemente.
São formados pelo verbo auxiliar to have (have/has) conjugado no Simple Present (presente simples) + o particípio passado (Past Participle) do verbo principal.
Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Present Perfect Simple:
| I | have loved |
| you | have loved |
| he/she/it | has loved |
| we | have loved |
| you | have loved |
| they | have loved |
- He has loved her during his entire life. (Ele a amou durante toda a vida dele.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Has he loved her during his entire life? (Ele a amou durante toda a vida dele?) - INTERROGATIVE
- He hasn’t loved her during his entire life. (Ele não a amou durante toda a vida dele.) - NEGATIVE
Present Perfect Continuous or Progressive (Presente Perfeito Contínuo ou Progressivo): expressa ações contínuas desde o passado até o presente ou que terminaram há pouco tempo.
É formado pelo verbo to have (have / has) conjugado no Simple Present (presente simples) + o verbo to be conjugado no Present Perfect (presente perfeito) + o gerúndio (-ing) do verbo principal.
Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Present Perfect Continuous:
| I | have been loving |
| you | have been loving |
| he/she/it | has been loving |
| we | have been loving |
| you | have been loving |
| they | have been loving |
Exemplos:
- She has been loving the new car. (Ela tem amado o carro novo.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Has she been loving the new car? (Ela tem amado o carro novo?) - INTERROGATIVE
- She hasn’t been loving the new car. (Ela não tem amado o carro novo.) - NEGATIVE
Past Perfect (Passado Perfeito Simples): expressa ações no passado que ocorreram antes de outra ação no passado.
É formado verbo auxiliar to have (had) conjugado no Simple Past (passado simples) + Past Participle (particípio passado) do verbo principal.
Segue abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Past Perfect:
| I | had loved |
| you | had loved |
| he/she/it | had loved |
| we | had loved |
| you | had loved |
| they | had loved |
Exemplos:
- She had loved Tom before she married Bob. (Ela tinha amado o Tom antes de se casar com o Bob.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Had she loved Tom before she married Bob? (Ela tinha amado o Tom antes de se casar com o Bob?) - INTERROGATIVE
- She hadn’t loved Tom before she married Bob. (Ela não tinha amado o Tom antes de se casar com o Bob.) - NEGATIVE
Past Perfect Continuous or Progressive (Passado Perfeito Contínuo ou Progressivo): expressa a continuação (duração) de ações no passado, que ocorreram antes de outra ação no passado.
Ele é formado pelo verbo to have (had) conjugado no Simple Past (passado simples) + verbo to be (been) conjugado no Past Perfect (passado perfeito) + gerúndio do verbo principal.
Confira abaixo, a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Past Perfect Continuous:
| I | had been loving |
| you | had been loving |
| he/she/it | had been loving |
| we | had been loving |
| you | had been loving |
| they | had been loving |
Exemplos:
- She had been loving studying there. (Ela estava adorando estudar lá.) – AFFIRMATIVE
- Had she been loving studying there? (Ela estava adorando estudar lá?) – INTERROGATIVE
- She hadn’t been loving studying there. (Ela não estava adorando estudar lá.) – NEGATIVE
Future Perfect (Futuro Perfeito): expressa ações que estarão terminadas em um determinado tempo futuro.
É formado pelo verbo auxiliar to have conjugado no Simple Future (futuro simples) + o particípio do verbo principal:
Veja abaixo a conjugação do verbo to love (amar) no Future Perfect:
| I | will have loved |
| you | will have loved |
| he/she/it | will have loved |
| we | will have loved |
| you | will have loved |
| they | will have loved |
Exemplos:
- They will have loved going to the concert. (Eles terão amado ir ao show.) - AFFIRMATIVE
- Will they have loved going to the concert? (Eles terão amado ir ao show?) - INTERROGATIVE
- They won’t have loved going to the concert. (Eles não terão amado ir ao show.) - NEGATIVE
Future Perfect Continuous or Progressive (Futuro Perfeito Contínuo ou Progressivo): expressa a continuação de ações que serão terminadas em determinado tempo no futuro.
É formado pelo Future Perfect do auxiliar to be (will have been) + radical do Presente Participle (Particípio presente) do verbo principal acrescido da terminação –ing.
Confira na tabela abaixo o verbo to love (amar) conjugado no Future Perfect Continuous:
| I | will have been loving |
| you | will have been loving |
| he/she/it | will have been loving |
| we | will have been loving |
| you | will have been loving |
| they | will have been loving |
Exemplos:
- He will have been loving his wife for 30 years next year. (Ele estará amando a esposa dele há 30 anos no ano que vem.) - AFFIRMATIVA
- Will he been loving his wife for 30 years next year? (Ele estará amando a esposa dele há 30 anos no ano que vem?) - INTERROGATIVA
- He won’t have been loving his wife for 30 years next year. (Ele não estará amando a esposa dele há 30 anos no ano que vem.) – NEGATIVA



Comentários
Postar um comentário